








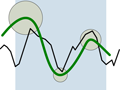
Time-series graphs are often used to visualize phenomena that change over time. Common tasks include comparing values at different points in time and searching for specified patterns, either exact or approximate. However, tools that support time-series graphs typically separate query specification from the actual search process, allowing users to adapt the level of similarity only after specifying the pattern. We introduce relaxed selection techniques, in which users implicitly define a level of similarity that can vary across the search pattern, while creating a search query with a single-gesture interaction. Users sketch over part of the graph, establishing the level of similarity through either spatial deviations from the graph, or the speed at which they sketch (temporal deviations). In a user study, participants were significantly faster when using our temporally relaxed selection technique than when using traditional techniques. In addition, they achieved significantly higher precision and recall with our spatially relaxed selection technique compared to traditional techniques.